|
StateFS
|
|
StateFS
|
StateFS is the syntetic filesystem to expose current system state provided by StateFS plugins as properties wrapped into namespaces.
Plugins are files (shared libraries etc.) be loaded by loaders - shared libraries, used to expose StateFS Provider API API from providers. Native provider can expose this C Provider API API itself.
StateFS provider is a shared library exposing statefs_provider_get function. To appear in statefs directory tree it should be Provider Registration registered.
Statefs provider API is used by statefs server to access provider information tree and properties data.
Provider should define statefs_provider_get() function, it is used to get provider's root statefs_provider structure for the first time.
StateFS information tree consists of nodes, node type is determined by statefs_node.type. Each node has optional metadata (array). There is a single root node (statefs_provider), namespace nodes (statefs_namespace) and property nodes (statefs_property).
Many provider structures has pointer to optional release function called by server to release resources associated with this structure.
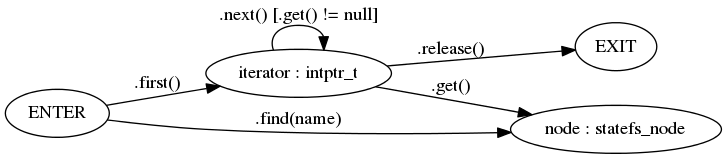
Root node and namespace nodes can have children nodes and are called branch nodes (statefs_branch). Property nodes are tree leafs.
Server accesses child node by name using statefs_branch.find(). Iteration through all child nodes is performed by means of opaque iterator (implementation is provider specific) retrieved by means of statefs_branch.first() and traversed by means of statefs_branch.next(). Node itself is accessed by means of statefs_branch.get(). End of iteration is determined by statefs_branch.get() returning NULL. At the end server calls optional statefs_branch.release() to release resources allocated by iterator (if any).
Provider should expect parent node will be released by server only after all child nodes are released.
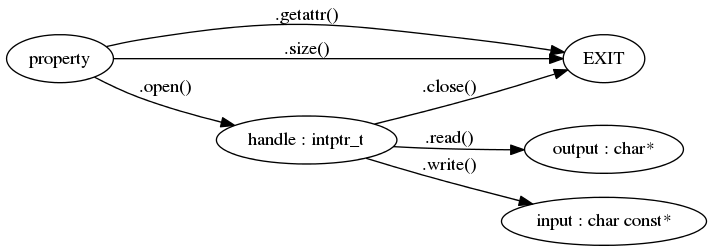
To access property data and attributes server uses api defined in statefs_provider.io. This API is done in a way resembling file access API but differs from it in details. The main idea is to give provider a way to organize property access in the way most suitable for it. So, provider can use some framework or implement API in its own specific way.
Loaders are used (obvioulsy :)) to load providers. Loader can e.g. prepare required environment for some native code provider (shared library), e.g. Qt code frequently needs Qt event loop to be executed in the "main" application thread - thread where soem Qt code was executed for the first time, so "qt" loader creates required environment and load Qt-based provider properly. Also loader can just get some file to be interpreted and to expose StateFS Provider API by itself etc. Loader API is deascribed Loader API here. Currently loader API is a C++ API but C API can be added easily. There is also default loader used in the case provider type is not specified. Default loader expects shared library exposing Provider Provider API API and just loads it.
Invoke
$ statefs register <path_to_provider_library>
This should be done once. Statefs performs introspection of the provider and saves this information in the configuration files used to create nodes associated with the provider on next statefs start w/o accessing provider library itself. This is done to avoid to load plugins before actual usage because it can take a time and statefs startup time should be minimal.
To unregister provider invoke
$ statefs unregister <path_to_provider_library>
Provider description is stored in human readable but easy to parse form of s-expression. It can be dumped using:
$ statefs dump <path_to_provider_library>
 1.8.3.1
1.8.3.1